- Cisco Anyconnect Two Connections Using
- Install Cisco Anyconnect
- Cisco Anyconnect Two Connections Online
- Cisco Anyconnect Two Connections Login
- Cisco Anyconnect Secure Download
- Cisco Anyconnect Open Two Vpn Connections
Duo with AnyConnect v4.6 or later on Cisco ASA can provide admins with insights into devices and their security posture. Check for device health and enforce policies to allow access to internal applications only from secure and healthy devices. Anyconnect uses 'ssl-vpn' by default, but it can be configured to run IKEv2 vpn also (i think, you have to place a connection profile on the VPN gateway to force anyconnect to use IKEv2). Also anyconnect is alble to run (and mybe will do so by default) 'ssl-vpn over dtls', which uses tunneling over udp/443 instead of tcp/443. I have the requirement where a piece of software that dials into the tax office uses cisco vpn client, but I also need my accountant to VPN to my office - requiring the cisco vpn client to make two concurrent connections. Internet connection after installing Cisco AnyConnect I have a problem on two computers after installing Cisco AnyConnect. After the installation of Cisco AnyConnect (Windows), the configuration of the connection then after disconnection there are problems with internet connection of programs: Google FileStream, Microsoft One Drvie, Microsoft.
Overview
The Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client consistently raises the bar by making the remote-access experience easy for end users. It helps enable a highly secure connectivity experience across a broad set of PC and mobile devices. This document provides information on the AnyConnect integration on Meraki appliances and instructions for configuring AnyConnect on the Meraki dashboard.
Client Download and Deployment
AnyConnect Authentication Methods
AnyConnect Troubleshooting Guide
AnyConnect on ASA vs. MX
FAQ
Feature
The AnyConnect VPN server on the MX uses TLS & DTLS for tunneling and requires AnyConnect VPN client version 4.8 or higher on either Windows, macOS, Linux, or mobile devices to terminate remote access connections successfully. The AnyConnect client negotiates a tunnel with the AnyConnect server and gives you the ability to access resources or networks on or connected to the AnyConnect server (MX). Unlike the AnyConnect implementation on the ASA, with support for other features like host scan, web launch, etc, the MX security appliance supports SSL, VPN, and other AnyConnect modules that do not require additional configuration on the MX. For more details, see AnyConnect on ASA vs. MX.
An AnyConnect Plus/Apex (termed or perpetual) license will be required to use AnyConnect on the MX when MX16.X firmware goes GA. Until then, if an MX upgrades to MX16, AnyConnect will be available as a feature. If a license is not linked when MX16 goes GA, AnyConnect will become unusable until a license is applied. More details on applying licenses will be available soon.
The MX supports L2TP/IPsec Client VPN and AnyConnect VPN simultaneously.
Caveats
AnyConnect is still in development, hence, there are certain caveats to keep in mind before enabling AnyConnect.

Supported MX models: MX600, 450, 400, 250, 100, 84, 68, 67, Z3, vMX
Future support: MX64, 65
Not supported: MX80, 90, 60, Z1
IPsec and AnyConnect share the same configured RADIUS and active directory servers
- The use of a server identity certificate with a custom hostname is not supported at this time. Currently, the MX will automatically enroll in a publicly trusted certificate using the Meraki Dynamic DNS host name on the dashboard network. Follow the instructions on this doc to change the hostname.
- A BETA firmware version is required. Known issues are listed below:
- Multicast on the LAN does not work as expected
- BGP routes do not show up on the dashboard route table but are present on the device
How to Enable AnyConnect on Your Dashboard
Having reviewed the caveats, upgrade your MX security appliance to the required firmware version.
- To enable AnyConnect, upgrade to the latest MX-16 firmware by navigating to Dashboard > Organization > Firmware upgrades. For more details on firmware upgrades see Managing Firmware Upgrades
- For further inquiries, email meraki-anyconnect-beta@cisco.com
AnyConnect Server Settings
MX Server certificate: The AnyConnect server on the MX uses TLS for tunnel negotiation, hence it needs a server identity certificate. Currently, when AnyConnect is enabled, the MX will automatically initiate a certificate-signing request to get a publicly trusted identity certificate; this is entirely transparent to the dashboard administrator. The MX uses the Meraki Dynamic DNS hostname when creating a CSR before getting it signed by a public CA. The resulting certificate renews automatically without any disruption in service.
Dashboard administrators do not have to worry about creating or transporting certificates or private keys to the MX or interacting with public CAs to get a CSR signed. At this time, we do not support uploading a server certificate or using a hostname other than the Dynamic DNS name.
Uploading a server identity certificate or using a hostname other than the Dynamic DNS name is not supported at this time. Please use the 'How to create a profile' documentation to create an alias for the Meraki DDNS hostname to ease connectivity for end-users.
DDNS hostname is configurable on MX Appliances in Passthrough/VPN Concentrator mode when AnyConnect is enabled.
To enable AnyConnect VPN, select Enabled from the AnyConnect Client VPN radio button on the Security Appliance > Configure > Client VPN > AnyConnect Settings tab. The following AnyConnect VPN options can be configured:
Hostname: This is used by Client VPN users to connect to the MX. This hostname is a DDNS host record that resolves to the Public IP address of the MX. The DDNS hostname is a prerequisite for the publicly trusted certificate enrollment. You can change this hostname by following the instructions here.
AnyConnect port: This specifies the port the AnyConnect server will accept and negotiate tunnels on.
Log-in banner: This specifies the message seen on the AnyConnect client when a user successfully authenticates. If configured, a connecting user must acknowledge the message before getting network access on the VPN.
Profile update: This specifies the AnyConnect VPN configuration profile that gets pushed to the user on authentication.
Certificate authentication: This is used to configure the trusted CA file that is used to authenticate client devices. This configuration is only required if you need to authenticate client devices with a certificate.
Authentication Type: This is used to specify authentication with Meraki Cloud, RADIUS, or Active Directory.
Group policy with RADIUS Filter-ID: This is used to enable dashboard group policy application using the filter passed by the RADIUS server.
RADIUS time-out: This is used to modify the RADIUS time-out for two-factor authentication and authentication server failover.
AnyConnect VPN subnet: This specifies the address pool used for authenticated clients.
DNS name servers: This specifies the DNS settings assigned to the client.
DNS suffix: This specifies the default domain name or DNS suffix passed to the AnyConnect client to append to DNS queries that omit the domain field. This domain name only applies to tunneled packets.
Client routing: This is used to specify full or split-tunnel rules pushed to the AnyConnect client device. You can send all traffic through VPN, all traffic except traffic going to specific destinations, or only send traffic going to specific destinations.
Default group policy: This is used to apply a default group policy to all connecting AnyConnect clients. For more details see Group Policies.
Authentication Methods
AnyConnect supports authentication with either RADIUS, Active Directory, or Meraki Cloud. For more details on authentication configuration, refer to AnyConnect Authentication Methods.
Note: Systems Manager with Sentry is not supported with AnyConnect.
Note: SAML authentication is not supported at this time.
Client Routing
i. Send all traffic through VPN
This is the same as full tunneling. All traffic from the client is sent over the VPN tunnel.
ii. Send all traffic except traffic going to these destinations
This is the same as full tunnel with exclusions, when configured, the client will send all traffic over the VPN except traffic destined for the configured subnet.
iii. Only send traffic going to these destinations
This is the same as spilt tunneling, when configured, the client will only send traffic destined for the configured subnet over the VPN. Every other traffic sent over the local network.
Local LAN access
Local LAN access is desired when the Full tunneling is configured (Send all traffic through VPN) but users still desire to their local network for printing, etc For example, a client that is allowed local LAN access while connected to the MX in full tunnel mode is able to print to a local printer at home. Internet traffic will still flow through the tunnel.
To enable local LAN access, two things need to be done. Local LAN access will not work if both conditions are not satisfied.
1. Configure the MX: Select 'Send all traffic except traffic going to these destinations' option on the Dashboard and configure a 0.0.0.0/32 route. This will cause the AnyConnect client to automatically exclude traffic destined for the user's local network from going over the tunnel.
2. Configure the Client: Enable Allow local LAN Access on the AnyConnect Client. This can be enabled manually or via the AnyConnect profile.
After connection, the user should see their local network subnet added as a non secure routes (destinations that should be accessed locally not via the VPN tunnel)
Group Policies
The need for access control over remote access connections cannot be over-emphasized. While some administrators use multiple address pools to segment users, others use VLAN tagging to existing subnets. From a Client VPN standpoint, multiple subnets or separate VLANs do not provide access control in itself. What segments users from talking to each other or other network resources is the presence and the enforcement of access rules. For example, if users are in different VLANs and access policies are not enforced somewhere, users could access anything.
AnyConnect on the MX does not support multiple VLANs or address pools for Client VPN users. However, the MX supports the application and enforcement of policies to AnyConnect users on authentication. It is also important to note that, from a Client VPN standpoint on the MX, having users on the same subnet does not mean they are in the same VLAN. Users are assigned a /32 address (one address) from the pool configured on Dashboard. Group Policies can then be used to limit users on the same AnyConnect subnet from talking to each other or other resources on the network.
Default Group Policy
Administrators can apply a global group policy to all users connecting through AnyConnect by selecting a configured policy from the default Group Policy drop-down menu. Group policies can be configured via Dashboard > Network-wide > Group Policies. Refer to Creating and Applying Group Policies for more details.
Note: If a default group policy set and group policy with Filter-ID is also enabled, the Filter-ID policy passed by the RADIUS server will take precedence over the default group policy.
Group Policies with RADIUS Filter-ID
AnyConnect supports the application of dashboard-configured group policies to AnyConnect users when authenticating with RADIUS. This is achieved using the RADIUS Filter-ID attribute. To set this up on your MX:
Create group policies on Dashboard > Network-wide > Group Policies. Specify rules within the policy. Multiple group policies can be mapped to different user groups on the RADIUS server. In this example, we are matching CONTRACTOR policy to CONTRACTOR user group.
Enable the Filter-ID option on the dashboard. This option is only configurable if you are authenticating with a RADIUS server.
Configure the RADIUS server to send an attribute in its accept message containing the name of a group policy configured in dashboard (as a String). Commonly, the Filter-ID attribute will be used for this purpose. The screenshot below shows a network policy in Windows NPS, configured to pass the name of a dashboard group policy ('CONTRACTOR') within the Filter-ID attribute:
The RADIUS server is configured with the group policy 'CONTRACTOR' defined on dashboard. When a user in the group successfully authenticates, the 'CONTRACTOR' group policy name for the authenticated user will be sent in the RADIUS accept message, allowing the MX to apply the requested policy to the user. The group policy name sent by the RADIUS server must match verbatim what is configured on the dashboard for policies to apply correctly. Currently, policies do not show up on Network-wide > Client list page if you have only a security appliance in your dashboard network, however, If you have a combined network, the policy will show under the 802.1X policy column.
Client VPN Connections
Client view:
You can see client stats and connection details by clicking on the graph in the bottom-left corner of the client.
Cisco Anyconnect Two Connections Using
Clients can also see available routes on the Route Details tab. Secure routes are accessible by the client over the VPN while nonsecure routes are not accessible by the client over the VPN. Nonsecure routes are visible when split-tunneling is configured.
Connection logs can be found under the Message History tab.
Dashboard view:
After configuring client VPN, to see how many users are connected to your network, navigate to Network-wide > Clients. All AnyConnect clients will be seen with the AnyConnect icon. You can filter by client VPN using the search menu.
Note: The MAC address seen on the client list is randomly generated; it is not the actual MAC address of the AnyConnect client.
AnyConnect Event Logging
To see all available events, navigate to Network-wide > Event log and filter the 'Event type include' field by AnyConnect.
To see log-on and log-off events, go to Dashboard > Network-Wide > Event logs and filter by VPN client connected and VPN client disconnected.
Dashboard API Support
APIs can be used to configure or return the AnyConnect server settings on the MX. Navigate to Dashboard > Help > API docs - AnyConnect VPN Settings for more information.

Number of Supported Sessions per MX Model
Below is the number of sessions allowed per MX model. When the limit is reached, new sessions will not be formed.
| Model | MX450 | MX250 | MX100 | MX84 | MX67/68 | Z3 | vMX S/M/L | vMX100 | MX600 | MX400 |
| Max sessions | 1,500 | 1,000 | 250 | 150 | 50 | 5 | 50/250/500 | 250 | 1,000 | 750 |
FAQ
Who signs the Meraki facilitated publicly trusted certificates?
A publicly trusted Certificate Authority.Can I use my own hostname or publicly trusted certificate on the MX as a server certificate?
No, only the Meraki DDNS hostname of the dashboard network is supported with publicly trusted certificates. There will be support for custom hostname certificates in future.How will AnyConnect be licensed on the Meraki MX?
Eventually, an AnyConnect Plus/Apex termed or perpetual license from Cisco will be required to use AnyConnect on the MX. Right now, AnyConnect can be used on the MX without a license.Will every MX model support AnyConnect eventually? If yes, when? If No, why?
AnyConnect is part of the wired-16 firmware, hence all models that can run wired-16 support AnyConnect, EXCEPT the MX64/65 models. Work is still in progress to support these models.Can I use AnyConnect profiles?
Yes, see the AnyConnect Profiles section. Only VPN profiles can be pushed via the MX. Others, like Umbrella profiles, will not be pushed via the MX.Can I configure different split-tunnel rules/VLANs/IP address pools for different sets of users?
No, not at the moment. However, you can use group policies when authenticating with RADIUS to apply access policies to a user or groups of users on authentication.Can I do certificate-based authentication?
Yes, as a combination with username and password. See the certificate-based authentication section. Certificate-only authentication is not supported at this time.Where can I download the AnyConnect client?
On the AnyConnect Settings page on dashboard in the Client Connection section or on cisco.com.How can I provide feedback on this feature?
Email meraki-anyconnect-beta@cisco.com or via the “make a wish” button on dashboard with “AnyConnect BETA” keyword.What are the current caveats/known issues with the AnyConnect feature & firmware?
See caveats sectionWhich features are supported? Any plans to support Umbrella, posture scan, 802.1x, etc?
VPN Only. Other AnyConnect modules that do not require additional server support can be used as well. e.g. DART, Umbrella. This module must be deployed and configured separately as the MX does not support web launch, client software deployment, or update at this time. See AnyConnect on ASA vs. MX for more details. Please email meraki-anyconnect-beta@cisco.com if you have any questions.Is IKEv2 supported on the MX when using AnyConnect?
No.Can I run L2TP/IPsec client VPN and AnyConnect VPN simultaneously on the MX?
Yes.Can I connect to the inside interface of the MX with AnyConnect? e.g. connect to the MX from the LAN side?
No, only connections on the WAN side/outside interface are supported at this time.When will AnyConnect GA?
This feature is firmware dependent, this means AnyConnect will GA when MX 16.X becomes GA.
The purpose of this guide is to provide guidelines on how to integrate Mideye two-factor authentication with Cisco AnyConnect SSL-VPN.
Requirements
A Mideye Server (any release). If there is a firewall between the Cisco ASA and the Mideye Server, it must be open for two-way RADIUS traffic (UDP, standard port 1812). Cisco ASA acts as a RADIUS client towards the Mideye Server. Hence, the Cisco ASA must be defined as a RADIUS client on the Mideye Server. Refer to the Mideye Server Configuration guide for information on how to define a new RADIUS client.
Password-change using MS-CHAP-v2
Since Cisco ASA supports MS-CHAP-v2 as authentication protocol, users that are about to have their password expired can change their password when login on using AnyConnect SSLVPN. To enable this feature Mideye Server release 4.3.0 or higher is required. For detailed instruction how to enable password-management, see section Enable MS-CHAP-V2.
Limitations with dynamic RADIUS-reject messages
The option to present RADIUS-reject messages dynamically from a RADIUS server was introduced in ASA version 8.3.x when using PAP as authentication method (default authentication method). This means that more information about failed login attempts is presented to the user, enabling users to solve login problems themselves. For example, if login fails due to the mobile phone not being reachable, the Mideye error message ’Phone not reachable, for help see [www.mideye.com/help]’ is displayed to the user instead of the default message ’Login failed’. Also information about token cards that are out of sync can be presented to the user. When using MS-CHAP-v2, dynamic reject messages will not be displayed from the Mideye Server, but instead from an internal database from your ASA. This means that reject messages can not be customised the same way as with using PAP. Challenge-messages will still be presented from the Mideye Server. For detailed instructions how to enable dynamic RADIUS-messages see section Dynamically display RADIUS-reject messages.
Prerequisites
This guide will not explain how to create a new connection-profile. Refer to Cisco-documentation how to setup your ASA to act as a remote-access VPN using AnyConnect.
The following steps will describe how create a new RADIUS-client on your Mideye Server, and how to create a new AAA-server and apply it to an existing connection profile with SSL-VPN enabled. All steps regarding the Cisco ASA will be executed from IOS accessed from either SSH, telnet or console.
Create a new RADIUS-client
Open “Configuration Tool” on your Mideye Server and click the “RADIUS-clients” tab. Click “New” and type the IP-address or hostname for your Cisco ASA. Click “LDAP Server” and assign LDAP-servers. Click “OK” followed by “Save” and “Close” to restart the services.
Create a new RADIUS-client for your Cisco ASA.
Create a new AAA-server using RADIUS
From Cisco IOS, access enter global configuration mode:
Create a new AAA-server using RADIUS:
Cisco-ASA (config)# aaa-server mideye-server protocol RADIUS
Assign IP, shared secret and timeout settings for the aaa-server:
Apply the created AAA-server to your existing SSL-VPN-profile:
Write the configuration made to memory:
Verify two-factor OTP functionality
To verify that RADIUS is setup correctly, logon to your Cisco ASA-firewall using ASDM and navigate to Configuration → RemoteAccessV P N → AAA/LocalUsers. Select the “Server Group” and the correct server name and click “Test”. Select “Authentication” and type a username and password that your RADIUS-server should be able to find via LDAP. An SMSOTP should be delivered followed by the following error-message:
This message appears because ASDM cannot handle challenge-response.
This chapter will explain various settings that can be made on the connection-profile.
Increase the timeout-value for the Cisco Anyconnect client
The default timeout-value for a connection-attempt initiated from a Cisco AnyConnect client is 12 seconds. For full functionality with Mideye RADIUS-server, the recommended timeout value is 35 seconds. This can only be changed using Cisco ASDM since all changes are written to an xml-file.
To change the timeout-value open ASDM and click “Configuration” → ”RemoteAccess VPN” → ”Network(Client)Access” → ”AnyConnectClientProfile”. Select the client profile used for Cisco AnyConnect and click “Edit”. If none exist, create a new one and assign it to the group-policy for AnyConnect then click “Edit”. Navigate to “Preferences (Part2)” and change the value “Authentication timeout (seconds) to 35 seconds. This new timeout-value will be downloaded automatically when connecting using Cisco AnyConnect client.
Change the timeout-value to 35 seconds (default 12 seconds).
Install Cisco Anyconnect
Last step is to add a Server Listing. Navigate to Server List and click “Add”. Add a host display name followed by the FQDN of the SSL-VPN URL. Save the configuration.
Note: First time changing this requires the endusers to first download the new .xml profile. The new timeout will function on their second connection using Anyconnect.
Dynamically display RADIUS-reject messages
Mideye error messages (and the default language) can be modified via Mideye Configuration tool, see screenshot below. RADIUS-reject messages on Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility will only work on Security Appliance Software Version 9.1(2) or higher using Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client 3.1.04066 or higher. This will only work when PAP is used as authentication-protocol. To enable the dynamic reject messages from ASDM complete the following steps.
- Click on “Configuration” followed by “Remote Access VPN”
- Click the “AnyConnect Connection Profile” and select the connection profile used for login with RADIUS followed by “Edit”
- Expand “Advanced” and click “Group Alias / Group URL”
- Check “Enable the display of RADIUS Reject-Messages on the login screen when authentication is rejected.”
Reject messages from Mideye RADIUS-server shown instead of “Login Failed”.
Reject messages dynamically displayed by the Mideye Server. These messages can be modified using configuration-tool on your Mideye Server.
Enable password-management (MS-CHAP-v2)
Starting from Mideye Server-release 4.3.0 and higher it is possible to manage passwords that are about to expire. This require further configuration on the Mideye Server (refer to Configuration guide). To enable this feature on Cisco ASA the following configuration need to be added.
Configure RADIUS-client to properly display special characters such as å, ä and ö
By default any created RADIUS client will use UTF-8 as encoding. To properly display special character such as å, ä and ö the encoding has to be changed to use ISO-8859- 1. This can be done by opening “Radiusconfigure” on your Mideye Server and select RADIUS Clients. Select the RADIUS-client created for ASA55xx and click modify. Click “Client configuration” and change “Encoding” to ISO-8859-1. Click “OK”, “Save” and “Close” to restart the Mideye Server.
This chapter explains optional configuration such as Dynamic Access Policy (DAP) with RADIUS-translation.
Cisco Anyconnect Two Connections Online
Dynamic Access Policy using RADIUS-translation
To further extend the functionality of RADIUS, Dynamic Access Policy (DAP) can be used to assign specific users or group permission from LDAP when logging in using AnyConnect. This require configuration on both the Mideye Server and Cisco ASA. When using DAP, all AnyConnect users will share the same IP-subnet but will be granted permission to certain network resources based on what group(s) they belong to in LDAP. Complete the following steps to enable RADIUS-translation with DAP:
Steps for Mideye Server:
- Open “Configuration Tool” on your Mideye Server and click the “LDAP RADIUS Translation” tab. Click “New”.
- Type the Distinguished name for a group containing users of a certain type (for example administrators) in the “LDAP Attribute Value” field. Select “CLASS” and click “Assign”. Add a suitable string for the group and click “OK”. Starting from Mideye Server release 4.2.3 LDAP-RADIUS translation can also be used with wildcard/Java Regular Expressions, e,g. CN=Mideye-administrators.*
Cisco Anyconnect Two Connections Login
Add DN, select CLASS and add a string for for the DN.
- Click “LDAP Servers” and select the LDAP Server being used and click “Modify”. Navigate to the “LDAP-RADIUS” tab and check” LDAP-RADIUS Translation” and type “memberOf” in the “LDAP Attribute Name:” field.
Enable LDAP – RADIUS Translation on the LDAP-server
- Click “Save” and “Close” to restart the service.
Steps for Cisco ASA:
- All configuration for DAP must be done using ASDM. Click “Configuration” → ”RemoteAccessVPN” → ”Network(Client)Access” → ”DynamicAccessPolicy”. Click “Add”.
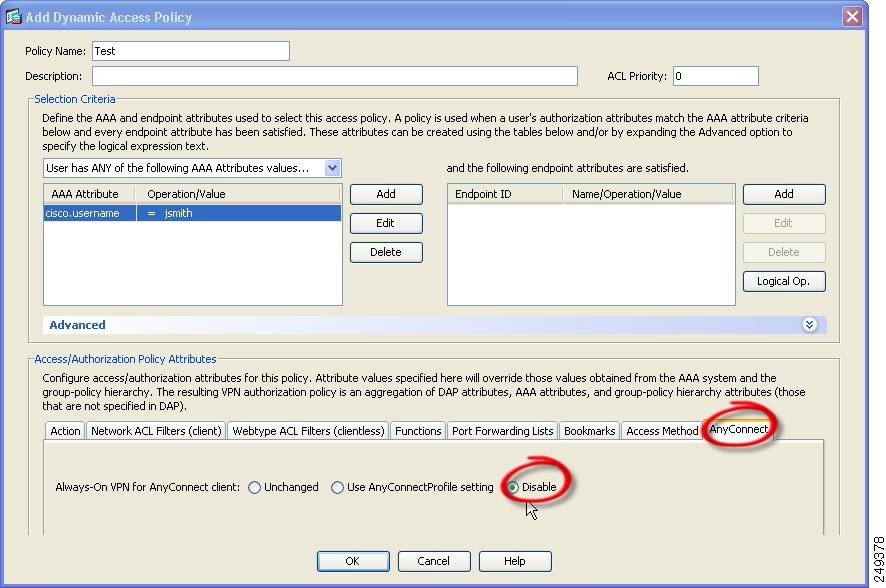
- Give the policy a suitable Policy name and change the “Selection Criteria” to “User has ALL of the following AAA…”
- Click the left “Add” button and change the AAA Attribute Type to “RADIUS” and type the Attribute ID 25. Add the same value as the string from the Mideye Server
- Click the “Network ACL Filters (client)” tab. Click “Manage” followed by “Add”. Create a new ACL and give it a suitable name. Select the ACL and click “Add” and add a new ACE. Add permissions to what networks or IP-addresses users should have access to. Click “OK” and finish the new DAP.
Manage permissions for the DAP.
Repeat steps 1-8 to add more groups. Verify that your DAP-policies work by connecting using AnyConnect. When verified change the default DAP “DfltAccessPolicy” to terminate all other connections. This can be done by selecting the default DAP-policy and click “Edit”. Change “Action” to “Terminate”.
Change the default DAP to terminate all other connections
Cisco Anyconnect Secure Download
Check RADIUS-logs
Check if anything is written to the Mideye RADIUS logs
If nothing is logged, verify that udp/1812 is allowed between your Cisco ASA and Mideye Server.
Contact Mideye support
Cisco Anyconnect Open Two Vpn Connections
For further support please contact Mideye support, support@mideye.com, +46854514750.
