Jul 24, 2020 If you are looking for the Anyconnect configuration example document, please refer to 'Configure AnyConnect VPN Client on FTD: Hairpining and NAT Exemption' document. Configure Step 1. Configure DHCP Scope in the DHCP Server. In this scenario, the DHCP server is located behind the FTD's inside interface. Anyconnect image disk0:/anyconnect-macosx-i386-4.1.02011-k9.pkg 2 anyconnect enable tunnel-group-list enable. Local pool for IP addressing of anyconnect clients. Ip local pool ACPOOL 172.19.0.1-172.19.0.254 mask 255.255.255.0. Nat exemption for excluding VPN traffic: nat (inside,outside) source static DC DC destination static AC AC. Hi Bob, I am having issues with drop out and data corruption using my companies VPN Cisco client. I have seen you managed to help others with this issue regarding a static IP address. I've tried every setting in the router to try and fix (DMZ/port forwarding/Port clamping/firewall off/etc).
- Cisco Anyconnect Windows 10 Download
- Cisco Anyconnect Secure Mobility Client Free
- Cisco Anyconnect Static Ip Download
- Cisco Asa Vpn Static Ip Client
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to configure the Cisco 5500-X Series Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) to make the DHCP server provide the client IP address to all the Anyconnect clients with the use of the Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) or CLI.
Prerequisites
Requirements
This document assumes that the ASA is fully operational and configured to allow the Cisco ASDM or CLI to make configuration changes.
Note: Refer to Book 1: Cisco ASA Series General Operations CLI Configuration Guide, 9.2 to allow the device to be remotely configured by the ASDM or Secure Shell (SSH).
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:

Cisco ASA 5500-X Next Generation Firewall Version 9.2(1)
Adaptive Security Device Manager Version 7.1(6)
Cisco Anyconnect Secure Mobility Client 3.1.05152
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Related Products
This configuration can also be used with Cisco ASA Security Appliance 5500 Series Version 7.x and later.
Background Information
Remote access VPNs address the requirement of the mobile workforce to securely connect to the organization's network. Mobile users are able to set up a secure connection using the Cisco Anyconnect Secure Mobility Client software. The Cisco Anyconnect Secure Mobility Client initiates a connection to a central site device configured to accept these requests. In this example, the central site device is an ASA 5500-X Series Adaptive Security Appliance that uses dynamic crypto maps.
In security appliance address management, you have to configure IP addresses that connect a client with a resource on the private network, through the tunnel, and let the client function as if it were directly connected to the private network.
Furthermore, you are dealing only with the private IP addresses that are assigned to clients. The IP addresses assigned to other resources on your private network are part of your network administration responsibilities, not part of VPN management. Therefore, when IP addresses are discussed here, Cisco means those IP addresses available in your private network addressing scheme that let the client function as a tunnel endpoint.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) in order to obtain more information on the commands used in this section.
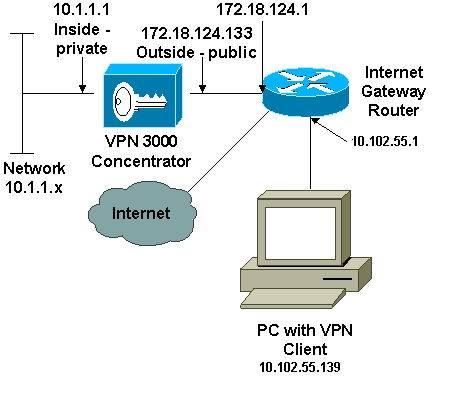
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
Note: The IP addressing schemes used in this configuration are not legally routable on the Internet. They are RFC 1918 addresses which were used in a lab environment.
Configure Cisco Anyconnect Secure Mobility Client
ASDM Procedure
Complete these steps in order to configure the remote access VPN:
- Enable WebVPN.
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > SSL VPN Connection Profiles and under Access Interfaces, click the check boxes Allow Access and Enable DTLS for the outside interface. Also, check the Enable Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client or legacy SSL VPN Client access on the interface selected in this table check box in order to enable SSL VPN on the outside interface.
- Click Apply.
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Anyconnect Client Software > Add in order to add the Cisco AnyConnect VPN client image from the flash memory of ASA as shown.
Equivalent CLI Configuration:
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > SSL VPN Connection Profiles and under Access Interfaces, click the check boxes Allow Access and Enable DTLS for the outside interface. Also, check the Enable Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client or legacy SSL VPN Client access on the interface selected in this table check box in order to enable SSL VPN on the outside interface.
- Configure Group Policy.
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Group Policies in order to create an internal group policy clientgroup. Under the General tab, select the SSL VPN Client check box in order to enable the SSL as tunneling protocol.
- Configure the DHCP Network-Scope in the Servers tab, choose More Options in order to configure the DHCP Scope for the users to be assigned automatically.
Equivalent CLI Configuration:
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Group Policies in order to create an internal group policy clientgroup. Under the General tab, select the SSL VPN Client check box in order to enable the SSL as tunneling protocol.
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > AAA/Local Users > Local Users > Add in order to create a new user account ssluser1. Click OK and then Apply.
Equivalent CLI Configuration:
- Configure Tunnel Group.
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Anyconnect Connection Profiles > Add in order to create a new tunnel group sslgroup.
- In the Basic tab, you can perform the list of configurations as shown:
- Name the Tunnel group as sslgroup.
- Provide the DHCP server IP address in the space provided for DHCP Servers.
- Under Default Group Policy, choose the group policy clientgroup from the Group Policy drop-down list.
- Configure DHCP Link or DHCP Subnet.
- Under the Advanced > Group Alias/Group URL tab, specify the group alias name as sslgroup_users and click OK.
Equivalent CLI Configuration:
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Anyconnect Connection Profiles > Add in order to create a new tunnel group sslgroup.
Subnet-Selection or Link-Selection
DHCP Proxy support for RFC 3011 and RFC 3527 is a feature introduced in the 8.0.5 and 8.2.2 and it has been supported in onward releases.
- RFC 3011 defines a new DHCP option, the subnet selection option, which allows the DHCP client to specify the subnet on which to allocate an address. This option takes precedence over the method that the DHCP server uses to determine the subnet on which to select an address.
- RFC 3527 defines a new DHCP suboption, the link selection suboption, which allows the DHCP client to specify the address to which the DHCP Server should respond.
Cisco Anyconnect Windows 10 Download
In terms of the ASA, these RFCs will allow a user to specify a dhcp-network-scope for DHCP Address Assignment that is not local to the ASA, and the DHCP Server will still be able to reply directly to the interface of the ASA. The diagrams below should help to illustrate the new behavior. This will allow the use non-local scopes without having to create a static route for that scope in their network.
When RFC 3011 or RFC 3527 is not enabled, the DHCP Proxy exchange looks similar to this:
With either of these RFCs enabled, the exchange looks similar to this instead, and the VPN client is still assigned an address in the correct subnet:
Configure the ASA with Use of the CLI
Complete these steps in order to configure the DHCP server to provide IP address to the VPN clients from the command line. Refer to Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliances-Command References for more information on each command that is used.
Learn about UCSD's expanded virtual private network (VPN) service, which lets you create protected connections to UCSD's network from remote locations.
VPN Use During Temporary Remote Work Directives Spring 2020
In response to the surge in remote workers, IT Services has significantly upgraded the capacity and performance of the VPN service. As such you should feel free to rely on the VPN anytime you are working remotely. When connected to the VPN using the 2-Step Secured - allthruucsd group, all of the traffic to and from your home or remote computer has malware filtered exactly as any on-campus computer does. However, the VPN should not be used when you are not working, such as when a family member is using your personal computer. Note that most academic and student services do not not require you to be logged in to VPN. Faculty and staff are encouraged to use the VPN when working on administrative activities. Find information on VPN setup.
These services require VPN:
- Shared Network Drives
- Cognos/Tableau
- Remote Desktop to computers or VMs
- TN3270 (IFIS/ISIS)
- Library resources (requires 2-Step Secured - allthruucsd)
- Staging links to preview CMS websites (requires 2-Step Secured - allthruucsd)
- Canvas does not require VPN but is recommended if connecting outside the U.S.
- AccessLink
- TechWiki
- Some department-specific applications (iDocs, BAMTRAC, CRIS)
The UCSD VPN creates a virtual private connection over public networks using encryption and other security checks to help protect against computer data transmission interception. It also helps ensure only authorized users can access campus networks. With VPN, network computing traffic between your remote machine (off-campus or wireless) and campus passes over a single, encrypted connection, and your remote machine has a UCSD IP address.
Two-step login is required for VPN connections. Learn more about VPN and two-step login.
Note
Instructions for UC San Diego Health and Health Science VPN users can be found at mcvpn.ucsd.edu.VPN Services
Cisco Anyconnect Secure Mobility Client Free
- AnyConnect - Cisco software VPN client which offers the maximum capabilities and performance.
- EasyConnect - web-based VPN portal at https://vpn.ucsd.edu, which allows secure access to many campus services, electronic library resources, and remote desktop computing without requiring the installation of a software client.
Connect to UCSD's VPN using one of these options:
- VPN AnyConnect client — Download the client for secure access to UCSD services, including Library resources using:
- Conventional installation:
- EasyConnect Web interface to access UCSD services (except the Libraries) — Easily and securely access UCSD services without installing the client. Mac OS X users: EasyConnect Web interface should only be used with computers running Mac OS X 10.8 and newer. Older versions of Mac OS X are no longer supported.
- Go to https://vpn.ucsd.edu
- Enter your Active Directory (AD) username and password.
- Select EasyConnect from the Group drop-down menu, and click Sign On.
- You now can access campus services by clicking a link from the list, such as:
- Campus Exchange (Outlook Web Access)
- Campus Network Status
- Link Family (FinancialLink, TravelLink, etc.)
- SysWiki (for campus system administrators)
You can also access services by typing a URL in the Address field.
- iPhone/iTouch/iPad 6.0.x and above
- Set up your iPhone or iPad to access the VPN.
To reset your Active Directory (AD) username or password, go to https://adweb.ucsd.edu/adpass or contact your department's system administrator.
VPN Pools
- The VPN service offers the ability to create department-specific pools, which can be used to control access to departmental resources. Please contact your IT support staff for additional information on accessing or using pools for your department. If you do not have IT support staff, then contact the ITS Service Desk.
- To access a VPN pool, when logging in to the VPN, enter your username followed by '@' the pool name. For example, to access the ITS pool, enter 'username@ITS'.

Cisco Anyconnect Static Ip Download
For additional technical info on the VPN service, please see the VPN article on the TechWiki.
Cisco Asa Vpn Static Ip Client
